Published: Aug 17, 2022
monetisation opportunities in the 5G era
Over the coming years, Telcos, System Integrators and Enterprises will be looking to capitalise on the maturing 5G network and invest heavily in infrastructure, technology, and applications. From exploring new use cases to refreshing traditional business models, we are witnessing transformation through 5G in almost every vertical. However, the path to profitability is not always clear to everyone. We examine several exciting monetisation opportunities key stakeholders can capitalise on with the advent of 5G.
1. End-to-end 5G security for enterprises
While 5G brings about major benefits to enterprises through enhanced speed, connectivity and latency, heterogeneous environment, new networking paradigms and novel use cases makes 5G vulnerable to new security threats. This has resulted in a growing number of attacks that enterprises all around the world face. These threats can lead to widespread distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, physical hardware hijacks and even complete shutdown of systems.
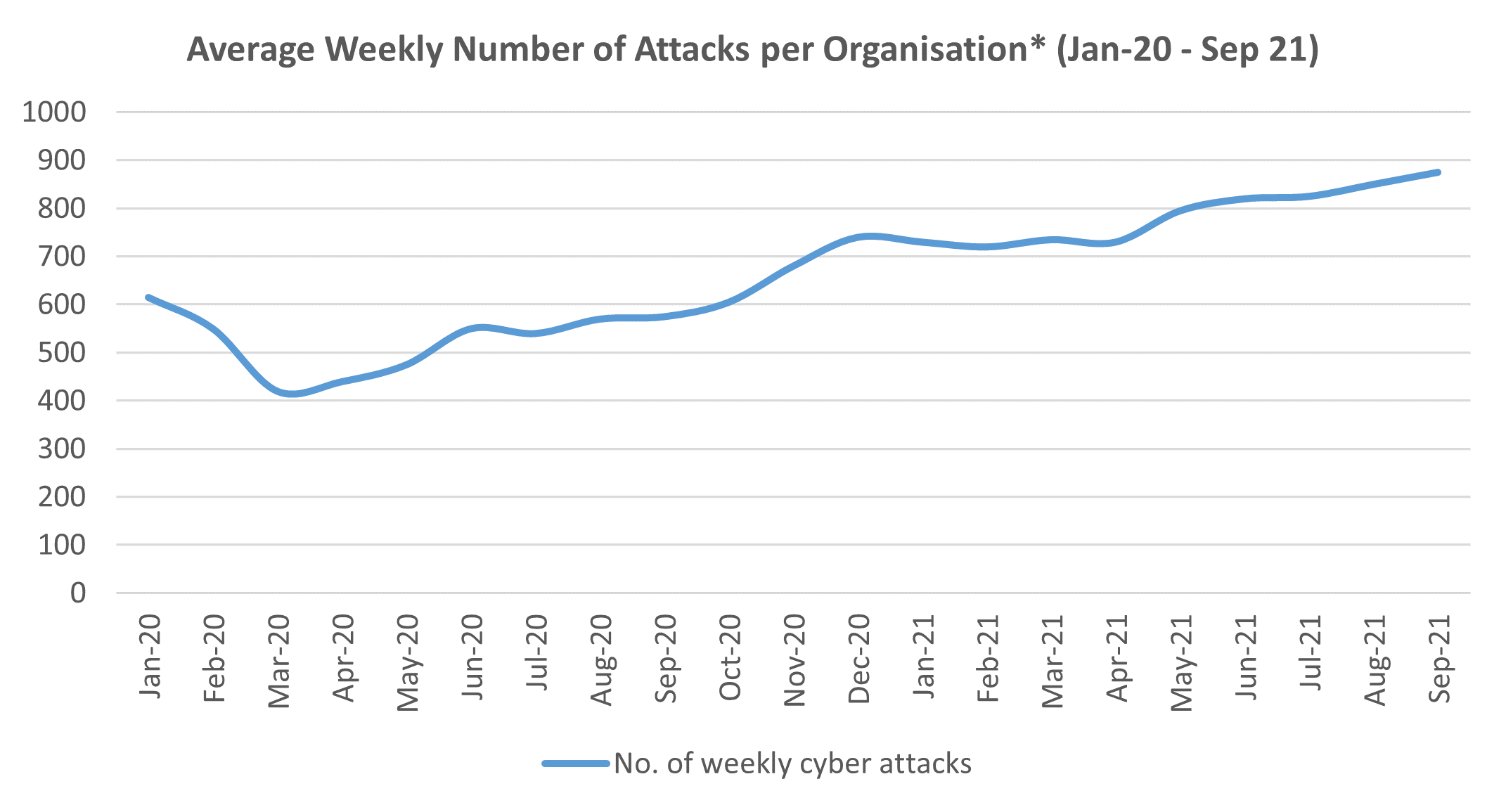
*North American organisations
Source: Check Point Software Technologies
This brings about the first key opportunity: End-to-End (E2E) security for enterprises. E2E security deals with aspects of authentication, integrity, key management, and confidentiality across the wide reach of 5G networks. This means that for E2E security to be effective, it should not only be flexible but scalable across the entire network to deliver mission-critical security.
Besides technologies linked to 5G, other elements within the 5G network needs to be highly secure. 5G Threats will emerge across RAN, Core, MEC and DC and public cloud as well as within IT, OT, and across Telco and Cloud. Therefore, E2E security must encompass endpoint security for various network slices, application, and device security, Radio Access Network (RAN) or telco security (provision of radio connections linking devices and endpoints to networks), 5G core network (including day-to-day operations and management elements) security, and Edge Cloud security.
Figure 1. End-to-End security in enterprise on 5G network
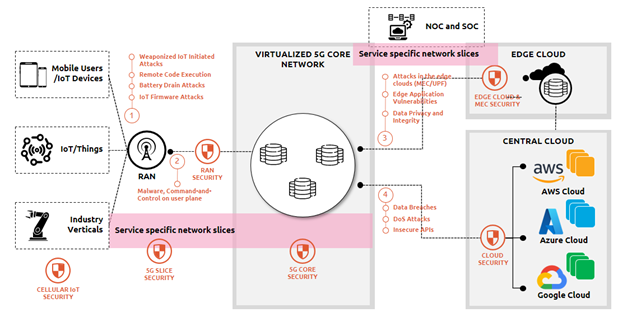
Source: NCS research
Various applications interact with the 5G network used for enterprise systems. Some examples of these applications include connected cars and smart grids. In such venues, it is critical to protect data privacy as well as the operation of each venue as threats to the system can compromise customer privacy and safety (i.e., attack on software and controlling multiple connected cars, shutting down grids supplying energy to cities).
With the introduction of 5G and new technologies, enterprises will need to ramp up their E2E security and cover a broader attack surface. This presents a unique opportunity for security providers to provide comprehensive, exhaustive, and dynamic E2E security solutions for enterprise 5G and its applications.
2. Identification (ID) management of Things:
One trend we observe is the massive growth of IoT-linked devices. As a critical enabler of IoT, 5G enables faster speeds, greater capacity, and reliable connectivity to unlock the potential of IoT ecosystems and connected devices. On the other hand, devices employed by both enterprises and consumers are evolving to be smaller, smarter, and more personal. The convergence of IoT technologies and identity management could become the next key opportunity area of growth.
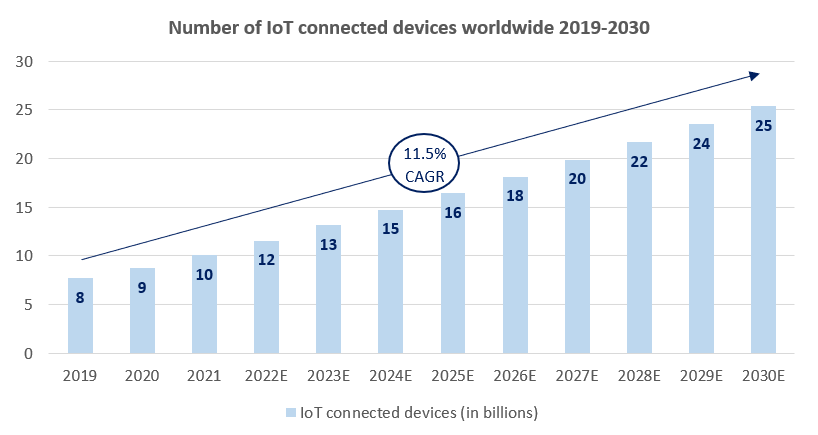
Source: Statista
Many devices we interact with today, from cars to handheld devices, are uniquely identified to access the network through international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI). While the purpose of doing so is for authorisation and access, over time the sheer volume and growth of “Things” with an identification grew to the point where it makes commercial sense to properly employ ID management. This creates an opportunity for players to step in and provide ID management for Things.
In France, Orange S. A. has forged ahead and developed in-house identity platforms as part of a wider access management strategy (Thales, 2020). This initiative is aimed at centralising and securing the data of millions of its customers. There are several compelling reasons why identity management is not only a lucrative opportunity but a strategic one in the 5G era. For one, maintaining up-to-date identities and access management are the most immediate use cases that scales marginally as more devices and connections are deployed. Digital identity management is the basis for secure data transfer and allows granular access control to manage and exchange data between resources, applications, and data owners. These form the foundation for personal customer engagement. Therefore, adopting the right identity management strategy will grow revenues through better customer service and longer customer lifetime value.
5G will reach far and wide and impact many sectors, especially those that manage large numbers of devices and applications (e.g., government, manufacturing, healthcare etc.). Hence, the ripening opportunity to rollout ID management of Things to provide stronger security and access management is critical in the scaling of IoT devices and digital identities.
3. 5G Data tsunami:
The 5G era will bring about ubiquitous high speeds, high data throughput and massive connectivity. With smarter devices, more details and data can be easily captured resulting in a data storm that leads to an impending data tsunami. Key technologies, such as AI, Cloud, and MEC are greatly enhanced by 5G. These technologies further perpetuate the rise in data traffic, forcing industries and their device ecosystems to evolve and capitalize on new opportunities.
A plethora of opportunities driven by enhanced 5G connectivity such as improved automation, data monetisation, and edge compute, will experience massive growth. As industries and device ecosystems become ‘smarter’, connected applications and existing solutions will begin to evolve and capitalise on this surge of data traffic. This creates larger dependencies on data centres, virtual machines and MEC. Emergence of use cases such as connected buildings and smart girds also accelerates the production and availability of data.
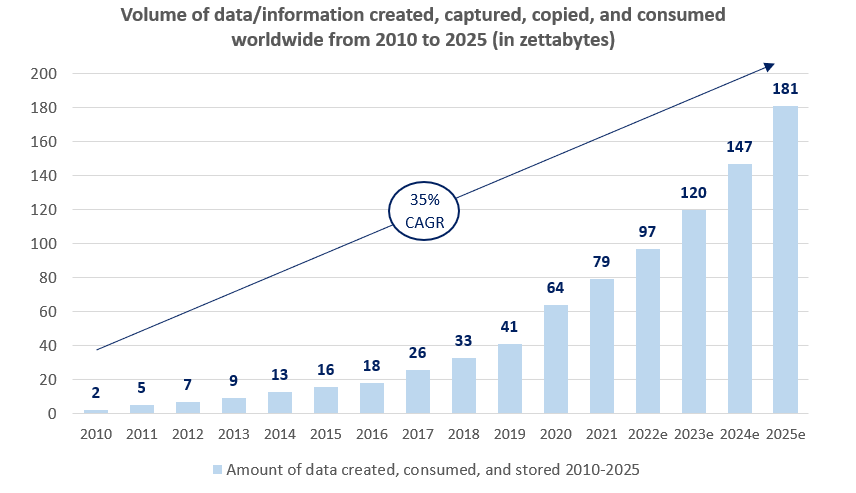
The data tsunami will make it impractical for humans to perform analysis efficiently. This creates another unique opportunity for players to capitalise on the production, collection, analysis, and management of big data utilising Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms. This can take the form of building out scalable data architectures and analytic tools that can capture insights to make better decisions quicker.
Several industries are set to benefit from the tsunami of data. In manufacturing, enterprises who have begun taking steps to innovate in line with Industry 4.0 will trial and implement a host of new use cases with the goal of increasing productive and efficiency. In one factory, automation helped a manufacturer reduce product rework rate from 25 to 15 percent by utilising data collected from production machines to prevent errors. This initiative is projected to save about EUR 27 million annually savings (Ericsson, 2018). These innovations will inevitably cause a surge in data transfers and require strong underlying infrastructural support and scalable data architectures to be effective in transforming the industry.
It seems that with greater connectivity and network speeds through 5G comes greater data usage and traffic. Therefore, we believe that the maturing of 5G and emergence of greater data transfers will create a massive opportunity for end-to-end data management.
4. Prefabricated 5G solutions:
5G enables many new technologies that in turn paves the way for the development of many new use cases. For enterprises, the quicker they are to adopt and go-to-market with newer technologies, the better position they would be to capture greater share of the market and hone a competitive edge.
While it is not known if there will ever be a ‘killer application’ for 5G, the ability to enable a quicker pace of innovation could be of greater priority for enterprises now. Use cases and solutions can be developed faster by ‘mixing and matching’ from different solution components, akin to Lego blocks – where prefabricated solutions, like Lego, can be pre-built/pre-fixed and delivered more quickly.
With pre-configured and prefabricated 5G industry-specific solutions, enterprises will be able to more easily deploy solutions that are both modular and scalable in nature. A central App Marketplace, like Singtel’s 5G Paragon, offers a suite of industrial applications orchestrated on a single platform to deliver powerful enterprise tools for different network slices (Singtel, 2022). Solutions such as these also reduce project start-up cost and therefore overall risk. As a result, enterprises can quickly deploy tried and tested 5G-enabled solutions that enables them quicker time-to-market rather than building solutions from with uncertain payoff.
One thing is for sure, that the 5G era will enable broad transformations across technologies and processes in a quick time. To capitalise this growth, enterprises can better prepare themselves by prioritising quicker time-to-market and constant validation and curation of the most effective solutions that fit them.
References:
5G and IOT in 2022. Thales Group. (2022). Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://www.thalesgroup.com/en/markets/digital-identity-and-security/iot/resources/innovation-technology/5G-iot
Allan, K. (2022, February 18). 5G future trends to watch in 2022. IT PRO. Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://www.itpro.com/mobile/5g/362281/5g-future-trends-to-watch
An, X. (Ed.). (2020). 5G Industry Campus Network Deployment Guideline Version 2.0 21 October 2021. www.gsma.com. Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://www.gsma.com/newsroom/wp-content/uploads//NG.123-v2.0.pdf
Apte, P. (2021, June 11). Time to market: How 5G can improve speed to market. Verizon Enterprise. Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://www.verizon.com/business/resources/articles/s/how-5g-can-improve-speed-to-market/
Clement, J. (2020, February 28). Global Mobile Data Traffic 2022. Statista. Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/271405/global-mobile-data-traffic-forecast/
Columbus, L. (2018, May 23). 10 charts that will change your perspective of Big Data's growth. Forbes. Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://www.forbes.com/sites/louiscolumbus/2018/05/23/10-charts-that-will-change-your-perspective-of-big-datas-growth/?sh=5a8b9bb52926
Craven, R. (2020). Identity management: Increasing telcos' customer-centricity and revenues. Amdocs. Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://www.amdocs.com/insights/analyst-report/identity-management-increasing-telcos-customer-centricity-and-revenues
Ericsson. (2018). 5G Business Value - A case study on real-time control in manufacturing. Ericsson. Retrieved June 28, 2022, from https://www.ericsson.com/4aad73/assets/local/reports-papers/consumerlab/reports/2018/5g_for_industries_report_blisk_27062018.pdf
Kumari, K. A., Sadasivam, G. S., Gowri, S. S., Akash, S. A., & Radhika, E. G. (2018). An approach for end-to-end (E2E) security of 5G applications. 2018 IEEE 4th International Conference on Big Data Security on Cloud (BigDataSecurity), IEEE International Conference on High Performance and Smart Computing, (HPSC) and IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data and Security (IDS). https://doi.org/10.1109/bds/hpsc/ids18.2018.00038
Li, S., Iqbal, M., & Saxena, N. (2022). Future industry internet of things with zero-trust security. Information Systems Frontiers. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-021-10199-5
Maddison, J. (2021). Building end-to-end security for 5G networks. SecurityWeek. Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://www.securityweek.com/building-end-end-security-5g-networks
Main considerations for securing enterprise 5G networks. Trend Micro. (2021, July 15). Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://www.trendmicro.com/en_au/research/21/g/main-considerations-for-securing-enterprise-5g-networks.html
Mudrakola, S. (2021, March 30). 5G network slicing: Applications, use-cases, and future possibilities. TechGenix. Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://techgenix.com/5g-network-slicing/
Sinha, S. (2021, December 29). State of IOT 2021: Number of connected IOT devices growing 9% to 12.3 billion globally, cellular IOT now surpassing 2 Billion. IoT Analytics. Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://iot-analytics.com/number-connected-iot-devices/
Small, M. (2020). 5G and identity. KuppingerCole. Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://www.kuppingercole.com/blog/small/5g-and-identity
Wang, W. (2020, August 21). New 5G FWA trends for Homes & Enterprises. Huawei. Retrieved May 9, 2022, from https://www.huawei.com/en/technology-insights/publications/winwin/37/new-trends-5g-fwa-homes-enterprises

