Published: Oct 31, 2025
Green AI edge computing
Artificial intelligence continues to expand into every part of modern life — from healthcare to transportation, manufacturing to smart cities. Yet, as AI systems grow more complex, their environmental impact rises sharply. Training large models and transmitting vast data volumes to centralised data centres consumes significant energy and increases carbon emissions.
Edge computing offers a way to change that equation. By processing AI workloads closer to where data is generated — on local devices and at the network’s edge — organisations can drastically reduce data transmission, lower power consumption, and enable real-time decision-making. This shift, known as Green AI Edge Computing, transforms how sustainability and intelligence coexist in the digital ecosystem.
For NCS, edge computing is not theoretical; it’s practical and proven. From patient safety monitoring to smart traffic analytics and robotic navigation systems, NCS has deployed edge-based solutions that enhance performance while reducing the environmental footprint of AI operations. As sustainability becomes an operational priority across industries, edge computing will play a defining role in realising energy-efficient, intelligent systems built for scale.
Key takeaways
- Edge computing minimises energy use by reducing reliance on centralised data centres and shortening data transmission paths.
- Localised intelligence enables real-time processing for critical applications such as healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing, while cutting emissions.
- NCS edge solutions demonstrate measurable sustainability outcomes across projects in patient safety, smart mobility, and robotics.
- Green IoT (G-IoT) integration further enhances sustainability through energy-harvesting, interoperability, and circular economy principles.
- By combining Green AI and Edge Computing, organisations can build smarter, faster, and more sustainable ecosystems ready for Industry 5.0.
The challenge: Scaling AI sustainably
AI’s rapid adoption has amplified its energy demands. As algorithms grow larger and data volumes increase, the burden on centralised data centres continues to expand. These facilities require immense power for computation, cooling, and data transfer — all of which contribute to global carbon emissions. Green AI seeks to counter this trend by designing systems that are both intelligent and energy-efficient, balancing progress with environmental responsibility.
At the same time, many AI applications — from autonomous vehicles to medical monitoring — require real-time responsiveness that centralised systems can’t always deliver. Latency, bandwidth, and reliability remain limiting factors. To sustain AI’s growth while meeting energy and performance requirements, computation must move closer to where data is generated. This is where Edge Computing becomes critical.
The solution: Localised intelligence through Edge Computing
Edge computing decentralises AI by bringing processing and storage closer to the data source. This architecture dramatically reduces the amount of data transmitted to cloud servers and data centres, lowering both energy use and latency.
By embedding AI capabilities directly into devices, machines, and local gateways, Edge Computing enables real-time insights while reducing dependency on high-power infrastructure. The result: smarter systems that think locally and act sustainably.
NCS has demonstrated these benefits through multiple real-world deployments:
- Patient safety systems that use edge cameras to monitor and trigger emergency responses in real time, reducing data transmission and improving reaction times.
- Smart mobility solutions using edge-enabled vehicle cameras to analyse traffic flow directly at the source, optimising routing and reducing fuel consumption.
- Autonomous robotics navigation systems that leverage local processing for faster decision-making and lower energy use.
These projects highlight how localised intelligence can deliver both operational performance and measurable sustainability gains which are essential pillars of Green AI.
The impact across industries
Edge computing extends the principles of Green AI to multiple sectors, enabling a distributed and energy-aware model of intelligence.
Table 1 illustrates the breadth of edge computing’s role in driving sustainability across sectors connecting energy efficiency, operational intelligence, and ecological stewardship in one framework.

Table 1. Edge computing applications and their impact on sustainability.
Connecting Green AI, Edge AI, and Green IoT
An essential extension of edge computing’s sustainability impact is its integration with the Green Internet of Things (Green IoT) — a concept widely discussed in IEEE Access and Sensors research on energy-efficient device ecosystems [1]. Green IoT focuses on low-power, renewable-powered IoT devices that reduce carbon emissions and minimise environmental impact.
When combined with edge AI, these systems create the foundation of a circular digital economy, where data, devices, and energy continuously reinforce one another [2].
Together, Edge AI and Green IoT promote:
Decentralisation
Reducing dependency on large data centres and improving resilience through distributed intelligence [3].
Circularity
Extending device lifespans with predictive maintenance and resource reuse, supporting the principles of the circular economy.
Transparency
Providing real-time visibility across supply chains, enabling more responsible and informed decision-making.
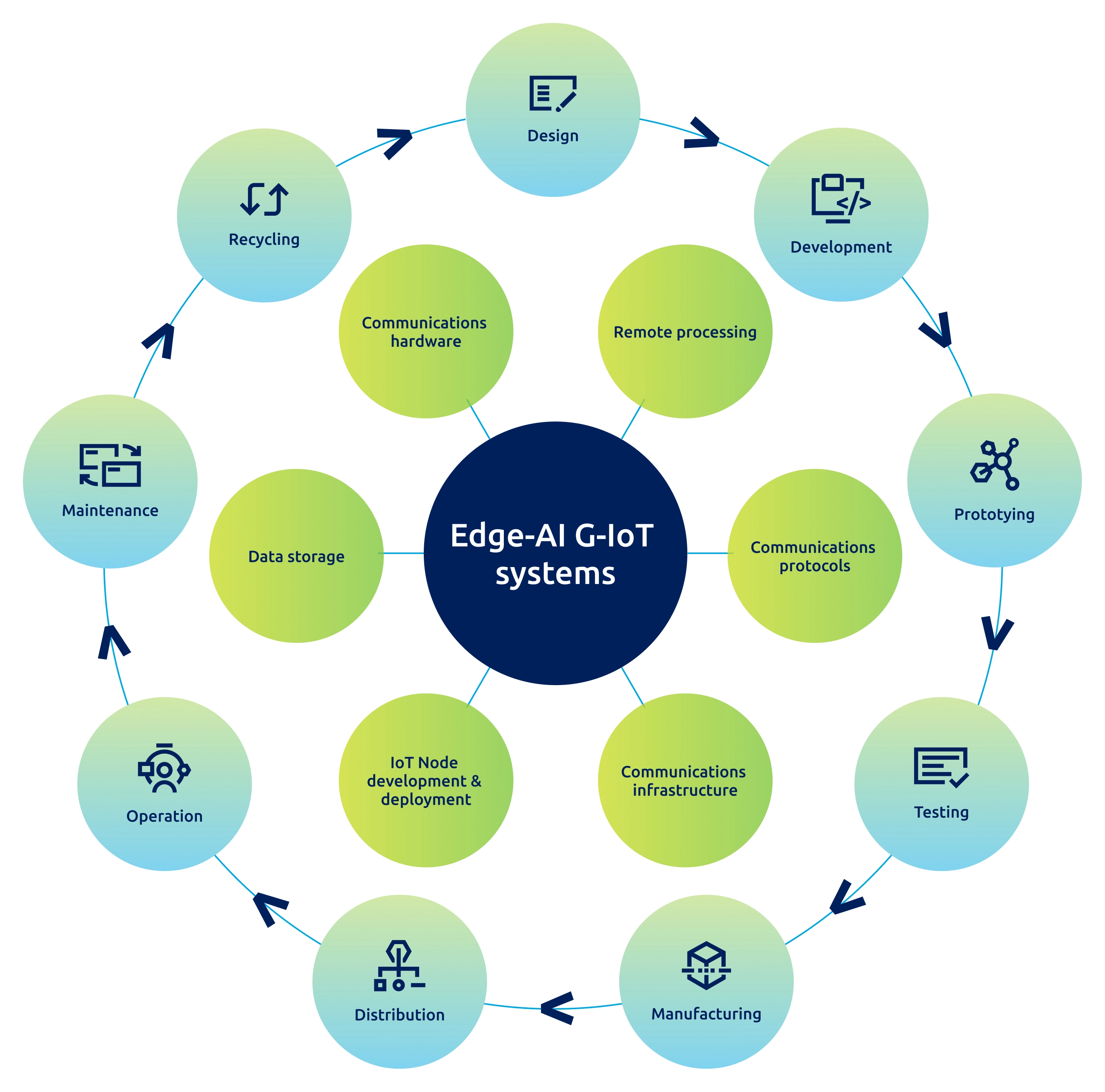
Figure 1: Main areas impacted by the combined use of Green IoT and Edge-AI in the context of Green AI.
This convergence empowers stakeholders, from manufacturers to policymakers, to optimise resources, improve productivity, and design sustainable systems that scale responsibly.
Overcoming the challenges of Edge AI
Despite its promise, implementing Green AI in edge environments poses several challenges:
- Energy limitations – Edge devices operate on constrained power budgets, making energy-aware algorithms essential.
- Hardware constraints – Limited compute, storage, and memory require lightweight AI models optimised for efficiency.
- Performance trade-offs – Balancing accuracy with energy consumption demands careful tuning and innovation.
- Collaboration gaps – Achieving true efficiency requires tight coordination between hardware, software, and AI researchers.
- Scalability – Solutions must adapt across industries and device types while maintaining consistent sustainability performance.
Solutions driving sustainable edge ecosystems
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-layered approach combining innovation, collaboration, and awareness.
- Energy-efficient algorithms – Model compression, pruning, and quantisation reduce computational demands without major accuracy loss.
- Hardware optimisation – Purpose-built low-power processors and energy harvesting technologies extend device life and reduce carbon load.
- Collaborative design – NCS advocates integrated development between AI researchers, engineers, and hardware partners to create end-to-end sustainable systems.
- Awareness and adoption – Industry education and partnerships encourage investment in sustainable AI R&D.
- Distributed and federated learning – Collaborative edge learning reduces dependence on centralised data and improves privacy while minimising energy consumption.
Together, these strategies can help organisations unlock the dual advantage of AI innovation and environmental sustainability.
Building smarter, cleaner, and closer intelligence
Edge Computing is redefining how intelligence is deployed — bringing computation closer to where data lives and transforming sustainability from an afterthought into a built-in advantage. By combining Green AI, Edge AI, and Green IoT, organisations can reduce their dependence on large data centres, cut transmission energy, and enable real-time decision-making that drives efficiency and resilience across industries.
For NCS, this is the next evolution of sustainable innovation.
Through its edge-enabled solutions in patient safety, smart mobility, and robotics, NCS helps clients achieve faster, cleaner, and more cost-effective operations. By embedding localised intelligence within infrastructure, NCS enables enterprises to meet performance demands while advancing long-term environmental goals. The result is a scalable ecosystem where technology, data, and sustainability converge to power the next generation of intelligent, low-impact systems.
Explore the edge of sustainable innovation
See how decentralised AI enables cleaner, faster decisions in our Green AI infographic.
References
[1] Arshad, R.; Zahoor, S.; Shah, M.A.; Wahid, A.; Yu, H. Green IoT: An Investigation on Energy Saving Practices for 2020 and Beyond. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 15667–15681.
[2] Askoxylakis, I. A Framework for Pairing Circular Economy and the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kansas City, MO, USA, 20–24 May 2018; pp. 1–6.
[3] Fraga-Lamas, P.; Lopes, S.I.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M. Green IoT and Edge AI as Key Technological Enablers for a Sustainable Digital Transition towards a Smart Circular Economy: An Industry 5.0 Use Case. Sensors 2021, 21, 5745. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21175745